Care Guide | MPA’s in Menorca
What are Marine Protected Areas (MAPs)?
A MPA is a legally protected zone in the sea, where human activities (especially fishing and extraction) are total prohibited (no-take reserves) or partially prohibited (partial reserves).
Why MPAs are created?
MPAs are created because of the need to preserve and recover marine ecosystems, biodiversity, and resources; and, in most of the cases, they are especially created to manage fishery resources.
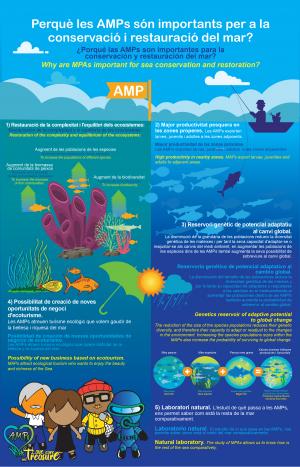
Why MPAs are important for sea conservation?
- Restoration of the complexity and equilibrium of the ecosystems:
-
- Increase of the species populations
- Increase of the biodiversity
- Increase in the biomass of the fish communities.
- High productivity in nearby zones
MAPs export larvae, juveniles and, adults to adjacent areas.
- Genetics reservoir of adaptive potential to global change
The reduction of the size of the species populations reduces their genetic diversity, and therefore their capacity to adapt or readjust to the changes in the environment.
Increasing the species populations sizes within the MAPs also increase the probability of surviving to global change.
- Possibility of new business based on ecotourism
MAPs attract ecological tourism who wants to enjoy the beauty and richness of the Sea.
- Natural laboratory
The study of MPAs allows us to know how is the rest of the sea comparatively.


What does the success of MPAs depend on?
- Active surveillance
- The success is greater in no-take reserves.
- Representatives of the marine ecosystems
- Big enough
- Numerous and connected
Network of Marine Protected Areas of the Balearic Islands and their biodiversity
Currently, the total marine surface with restrictions to preserve marine habitats and re-generate fishery resources in the Balearics Islands is 151,546 ha with 4,474ha of no-take areas. Moreover, the Balearic Islands have marine natural parks and areas of special interest for conservation (Natura 2000 European Network). Finally, the Menorca Biosphere Reserve has been recently extended to the sea, with a surface of 514,485 ha, and will be the biggest Marine Reserve in the Mediterranean.
Regulation
Each MPA has its own characteristics and regulation of activities, thus it is important to inform yourself before visiting them! Mainly, trawling and spearfishing are not allowed in most of them, while artisanal and recreational fishing is allowed with pre-established days and times, except in no-take areas.
Species biodiversity of the Balearic Sea
The Balearic Sea is still one of the best-preserved regions of the Mediterranean and new species are discovered every year. There are data of more than 1600 marine species, from the microscopic world to the most known species (~ 400 species of fish). Unfortunately many species are threatened; others, like the pen shell, are critically endangered; and others, such as the monk seal, have already become locally extinct in the Balearic Sea.
Habitats diversity of the Balearic Sea
The biodiversity of species is related to the diversity of the habitats where they live, and the Balearic Sea is also very rich in these, ranging from Posidonia meadows, mountains and submerged canyons, unexplored areas of more than 1000 m of depth, habitats of different types of corals, gorgonians gardens, etc.
Main threats to the Biodiversity of the Balearic Sea:
- Fishing activities without regulation or poorly managed
- Pollution
- Climate change
- Invasive species